Case 3 - Juan
- You are a clinician working in an emergency department in Queensland.
- The team leader receives a phone call from the Queensland Ambulance service (QAS) about a 2 year old male, Juan.
- Juan is being brought in unconscious with CPR in progress.
- QAS are 5 minutes away.
- No further information is available at this stage.
Questions to discuss about Juan’s case
- What are the key differences to consider in a paediatric resuscitation compared to adults? Consider role allocations.
- What are some of the anatomical, physiological, and psychological differences to consider in paediatric resuscitation when compared to adults?
- What weight (kg) would you estimate for Juan?
- What are the different ways of estimating a paediatric patient’s weight?
You have estimated Bella’s weight to be 12 kg. The team are starting to prepare drugs in anticipation for QAS.
- What is the appropriate method of determining resuscitation drug doses?
- Which drugs may be appropriate to prepare in this scenario?
QAS have arrived. CPR is ongoing. A pulse is not palpable. The monitor shows the following rhythm.
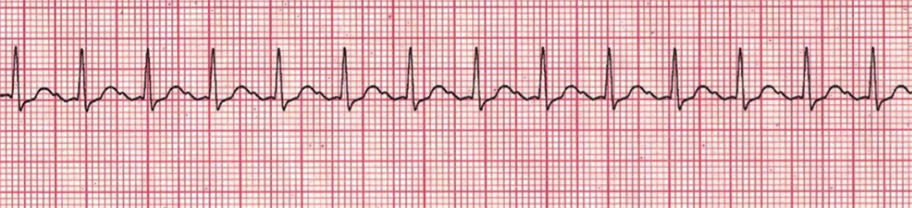
- What is this rhythm?
- How do you proceed?
Normal range for vital signs by age
Normal range for vital signs by age based on Childhood Early Warning Tool (CEWT)| Age | Heart rate (bpm) | Minimum Systolic BP (mmHg) | Respiratory Rate (bpm) |
|---|
| <1 year old |
100-159
|
<75
|
21-45
|
| 1-4 year old |
90-139
|
<80
|
16-35
|
| 5-11 year old |
80-129
|
<85
|
16-30
|
| 12-17 year old |
60-119
|
<90
|
16-25 |